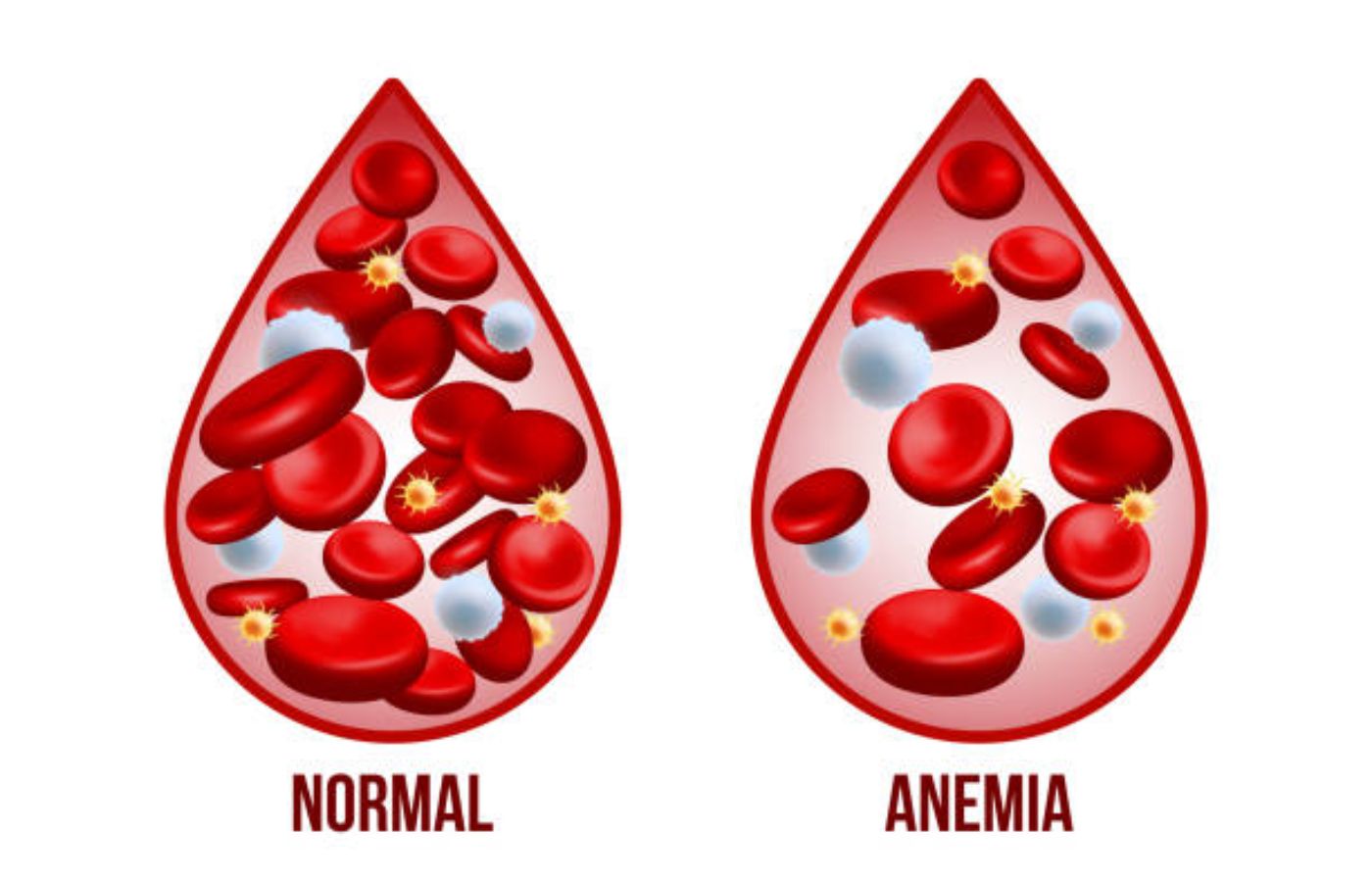
Anemia is a common blood disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when your body does not have enough healthy red blood cells to carry sufficient oxygen to tissues. Without enough oxygen, the body cannot function at its best. Anemia can range from mild to severe. Early detection and proper care are essential for good health.
Visit Now: https://www.diagnopein.com/CategoryBlogs/pathology
This guide explains the common symptoms of anemia, the main causes, and how anemia is diagnosed. It is written in clear, simple language for easy understanding.
Anemia happens when the number or quality of red blood cells in your blood is lower than normal. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. When hemoglobin levels drop, the body’s organs do not get enough oxygen.
Book Now: https://www.diagnopein.com/book-test/Pune
Anemia is not a disease itself. It is a sign of an underlying problem. Identifying the cause is key to proper treatment and management.
Symptoms of anemia can vary based on the type of anemia and how severe it is. In early stages, symptoms can be mild or even unnoticed. As anemia worsens, symptoms become more obvious.
Here are the most common symptoms:
Feeling tired all the time is the most frequent symptom. This happens because your body lacks enough oxygen to produce energy. Fatigue from anemia is often more intense than normal tiredness.
Weakness or lack of strength is common. Patients report difficulty in daily tasks that were once easy. This symptom can affect physical activity and concentration.
Shortness of breath occurs even with minimal exertion. This happens because the body tries to take in more oxygen to compensate for low blood oxygen levels.
Pale or washed-out skin is a visible sign. It is often noticed on the face, inner lips, or the beds of the fingernails. This is due to reduced red blood cells.
Anemia can cause dizziness or a sensation of spinning. This may worsen when standing up quickly. It is caused by low oxygen reaching the brain.
The heart works harder to deliver oxygen. This can cause a fast or irregular heartbeat, especially during physical activity.
Frequent headaches may occur when there is less oxygen reaching the brain. These headaches can be persistent and hard to relieve.
Poor blood circulation can make hands and feet feel cold. This is more noticeable in certain types of anemia.
In severe anemia, the heart must work harder to pump oxygenated blood. This strain can lead to chest discomfort or pain.
Difficulty concentrating and thinking clearly are common symptoms. The brain needs sufficient oxygen to function well. When oxygen is low, cognitive performance declines.
Anemia has many causes. Some are due to insufficient red blood cell production. Others occur when red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made. Some causes are temporary, while others are chronic.
Iron deficiency is the most common cause worldwide. Iron is needed to make hemoglobin. Without enough iron, the body cannot produce healthy red blood cells.
Common reasons for iron deficiency include:
Poor diet low in iron
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Pregnancy (increased iron demand)
Chronic blood loss (e.g., ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding)
Vitamin B12 and folate are critical for red blood cell production. A lack of these vitamins leads to poor red cell formation.
Causes include:
Poor diet
Gastrointestinal diseases (e.g., celiac disease)
Certain medications
Long-term illnesses can interfere with red blood cell production.
Examples:
Chronic kidney disease
Rheumatoid arthritis
Cancer
Heart failure
Some forms of anemia are inherited. These affect the structure or production of hemoglobin.
Hereditary causes include:
Sickle cell anemia
Thalassemia
Bone marrow is where blood cells are made. Diseases that affect the marrow can lead to anemia.
Examples:
Aplastic anemia
Leukemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Significant blood loss lowers red blood cell count.
Causes may include:
Trauma or surgery
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Some conditions destroy red blood cells faster than the bone marrow can replace them.
Underlying causes include:
Autoimmune disorders
Certain medications
Infections
Diagnosis begins with a clinical evaluation and lab tests. Early diagnosis improves outcomes. Your healthcare provider will perform simple tests to confirm anemia and find the cause.
The process usually begins with a detailed health history and physical exam. Your provider may ask about:
Symptoms
Diet
Family history
Medications
Chronic illnesses
Red blood cell count
Hemoglobin level
Hematocrit (percentage of red cells in blood)
Size and volume of red cells (MCV)
Low results often indicate anemia.
This test measures young red blood cells. It helps determine if the bone marrow is producing cells at the right rate.
Tests like:
Serum iron
Ferritin
Total iron binding capacity (TIBC)
These help confirm iron deficiency.
Low levels of B12 or folate point to deficiency anemia. These tests help differentiate the type of anemia.
Based on initial findings, your provider may recommend:
Bone marrow biopsy
Kidney function tests
Tests for hemolysis (e.g., Coombs test)
Genetic testing for hereditary anemia
These tests help determine the exact cause and severity.
Treatment depends on the type and cause of anemia. Common approaches include:
Iron supplements or a diet rich in iron-containing foods can correct iron deficiency.
Vitamin B12 or folate supplements are used when deficiencies are present.
Managing chronic diseases, controlling bleeding, or treating infections can improve anemia.
In severe cases, transfusions provide immediate relief by increasing red blood cells.
Certain anemias respond to medications that stimulate red blood cell production.
Seek medical care if you experience:
Persistent fatigue
Dizziness or shortness of breath
Unexplained weakness
Chest pain
Severe or worsening symptoms
Early evaluation can prevent complications.
Anemia affects many people but is often overlooked. Understanding the common symptoms, knowing the causes, and knowing how anemia is diagnosed are important steps in managing your health. If you suspect anemia, talk to your healthcare provider without delay.