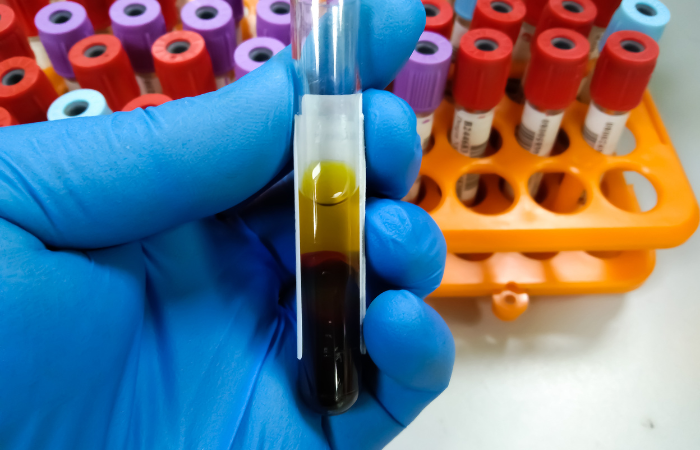
The Serum Ammonia Test is a diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of ammonia in the blood. Ammonia is a byproduct of protein metabolism, and under normal circumstances, it is processed by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. However, elevated ammonia levels can be a sign of various underlying health conditions, particularly related to the liver and brain.
The serum ammonia test is commonly used to diagnose conditions like hepatic encephalopathy, a condition where liver dysfunction leads to a buildup of toxins in the brain. Other conditions, such as liver cirrhosis, kidney failure, and metabolic disorders, can also result in elevated ammonia levels. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to confusion, lethargy, and in severe cases, coma, making the test an essential tool in early diagnosis and management.
Ammonia is produced when proteins are broken down in the intestines, and it is normally processed by the liver into urea, which is then excreted through the kidneys. However, when the liver is not functioning properly due to disease or damage, ammonia can build up in the bloodstream. A serum ammonia test measures the concentration of ammonia in the blood and helps doctors identify liver dysfunction, metabolic issues, or brain complications caused by high ammonia levels.
The test involves drawing a blood sample, which is then analyzed to determine the concentration of ammonia. It is a simple procedure that requires minimal preparation, but patients should inform their healthcare provider about any medications or conditions that may affect ammonia levels.
Normal ammonia levels generally range from 15 to 45 micromoles per liter (µmol/L), but this can vary depending on the laboratory conducting the test.
Elevated ammonia levels in the blood can indicate a range of medical conditions, including:
1. Liver Disease: Liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, and other liver-related issues may prevent the liver from processing ammonia, leading to high blood levels.
2. Kidney Failure: When the kidneys fail, they may not effectively eliminate ammonia from the bloodstream.
3. Metabolic Disorders: Certain genetic or metabolic disorders may impair the breakdown and removal of ammonia.
4. Hepatic Encephalopathy: This is a serious condition where toxins like ammonia build up in the brain, affecting mental function and potentially leading to coma.
If the test results indicate elevated ammonia levels, doctors may recommend additional tests, imaging, or biopsies to identify the underlying condition. Treatment depends on the cause of the high ammonia levels and can include medications, lifestyle changes, or procedures to manage liver or kidney health. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to stabilize the patient and reduce ammonia levels.
The serum ammonia test is typically recommended for patients who show symptoms of liver or kidney dysfunction, such as Confusion, disorientation, or mental status changes, Fatigue or weakness, Swelling in the abdomen or legs, Nausea or vomiting, Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes). If you have a history of liver disease or kidney problems, your doctor may recommend regular monitoring of your ammonia levels.
The serum ammonia test is an important diagnostic tool for identifying liver and metabolic conditions that can affect overall health. By measuring ammonia levels in the blood, doctors can diagnose problems early and provide targeted treatments to manage or reverse the underlying causes.
At Diagnopein Diagnostics, we offer comprehensive diagnostic services, including serum ammonia tests, to help detect and monitor liver and kidney function. Our expert team is committed to providing accurate, timely results to ensure that you receive the best care possible.
Contact Diagnopein Diagnostics today to schedule your serum ammonia test and take proactive steps toward maintaining your health.