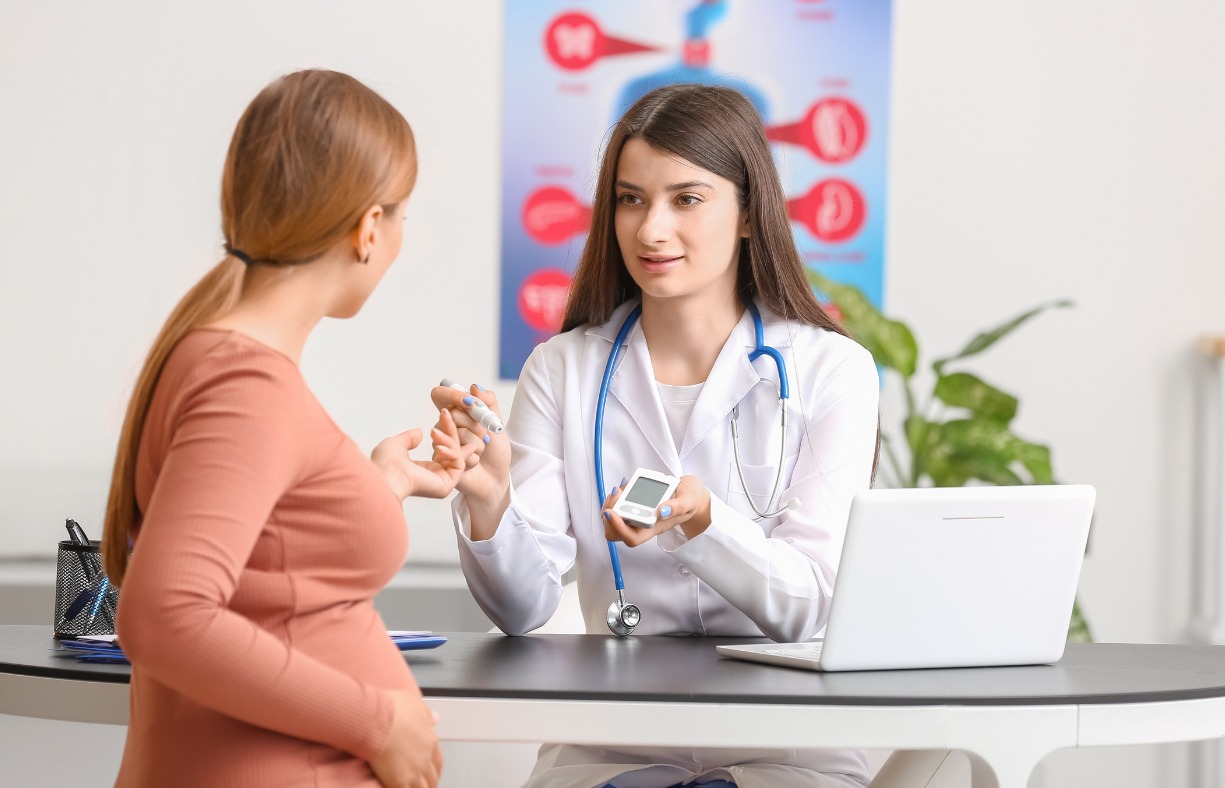
Pregnancy is an exciting and transformative time for expectant mothers, but it also comes with a range of challenges. One of the significant concerns for some women is diabetes during pregnancy, which can occur in various forms, including gestational diabetes. This condition can affect both the mother and the baby if left unmanaged, but with proper care and monitoring, it can be controlled effectively. If you're pregnant or planning to be, it's important to understand the types of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy, how they are diagnosed, and the steps you can take to manage the condition for a healthy pregnancy.
At Diagnopein, we provide comprehensive pregnancy diabetes tests and offer expert guidance on diabetes in pregnancy treatment. Our team is dedicated to supporting expecting mothers with the tools and information they need to manage diabetes safely and effectively throughout their pregnancy.
Diabetes during pregnancy refers to the onset of high blood sugar levels in a pregnant woman. It can develop in two primary forms:
1] Gestational Diabetes: This is the most common type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It typically occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels, resulting in high glucose levels in the bloodstream. Gestational diabetes usually appears in the second or third trimester and may resolve after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
2] Pre-existing Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes: Some women may have diabetes before becoming pregnant. If Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes is not well-controlled prior to pregnancy, it can lead to complications for both mother and baby.
It is crucial to understand that gestational diabetes in pregnancy is different from pre-existing diabetes, although both require careful management and monitoring.
Expecting mothers are typically screened for gestational diabetes between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. The screening process typically involves a pregnancy diabetes test, which may include the following:
1] Glucose Challenge Test (GCT): This involves drinking a sugary solution, followed by a blood test one hour later. If the blood sugar level is elevated, further testing is needed.
2] Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This Oral Glucose Tolerance Test involves drinking a sugary solution and measuring blood sugar levels at various intervals over a few hours. If blood sugar levels remain elevated at any point, gestational diabetes is diagnosed.
It’s important to attend these screenings to catch gestational diabetes early, as untreated high blood sugar can result in complications like preterm birth, high birth weight, and an increased risk of neonatal hypoglycemia (low blood sugar in the baby).

While every pregnancy is unique, some factors may increase the risk of developing gestational diabetes in pregnancy:
1] Age: Women over 25 are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
2] Obesity: Being overweight before pregnancy increases the risk of gestational diabetes.
3] Family History: A family history of diabetes can increase the likelihood of gestational diabetes.
4] Ethnic Background: Certain ethnic groups, including African-American, Hispanic, and Asian women, have a higher risk.
5] Previous Gestational Diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy are more likely to develop it again.
If you fall into one of these categories, it's important to discuss your risk with your healthcare provider early in your pregnancy and monitor your blood sugar levels closely.
Once diagnosed with diabetes in pregnancy, managing blood sugar levels is critical to ensuring a healthy pregnancy and reducing the risk of complications. Here are the key strategies for managing diabetes during pregnancy:
1] Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels -
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential in managing gestational diabetes. Your healthcare provider will advise you on when and how often to check your blood glucose. This helps you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and medication (if necessary), allowing you to make adjustments to your daily routine to keep blood sugar within target ranges.
2] Pregnancy Diabetes Diet -
A pregnancy diabetes diet plays a vital role in controlling blood sugar levels. Eating the right foods can help manage glucose levels and provide the nutrients both you and your baby need during pregnancy. Key components of a pregnancy-friendly diabetes diet include:
A] Balanced Meals: Focus on meals that include lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Aim for three main meals and healthy snacks throughout the day to prevent blood sugar spikes.
B] Limit Refined Carbs and Sugars: Foods like white bread, sugary drinks, and sweets can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. Instead, opt for whole grains and natural sources of sweetness like fruits.
C] Portion Control: Keep an eye on portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to higher blood sugar levels.
D] Frequent, Smaller Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals helps maintain consistent blood sugar levels and avoids large fluctuations.
E] Consult with a Dietitian: A registered dietitian can help you develop a meal plan tailored to your individual needs, ensuring both you and your baby get the right nutrients without compromising blood sugar control.
3] Exercise During Pregnancy -
Regular physical activity is crucial in managing diabetes during pregnancy. Exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively, which can lower blood sugar levels. Some safe exercises for pregnant women include: Walking, Swimming, Prenatal yoga, Low-impact aerobics.
Always consult with your doctor before starting an exercise program, as some activities may be better suited to your specific situation.
4] Medications (If Needed) -
In some cases, lifestyle changes may not be enough to control blood sugar levels, and medication may be required. Insulin is the most common medication used to control gestational diabetes in pregnancy, but oral medications may also be prescribed. Insulin injections are generally safe during pregnancy and help regulate blood sugar without affecting the baby.
If your healthcare provider recommends medication, follow their instructions carefully and continue monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly.
5] Regular Monitoring and Check-ups -
Throughout your pregnancy, it’s important to attend regular check-ups to monitor your blood sugar levels, track your baby’s growth, and assess any potential complications. Your doctor will perform routine ultrasounds to check for abnormal fetal growth and other signs of gestational diabetes complications.
At Diagnopein, we offer comprehensive monitoring and diagnostic services to help you manage diabetes in pregnancy effectively. Our expert team will guide you through the entire process and provide personalized care to ensure the best possible outcome for both you and your baby.
After childbirth, most women with gestational diabetes find that their blood sugar levels return to normal. However, it’s important to continue monitoring your health, as women who had gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Your doctor may recommend a postpartum glucose test to check your blood sugar levels and assess your risk. If you had gestational diabetes, adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying active can help reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes in the future.