Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is one of the most commonly used diagnostic tools in modern medicine. It helps doctors view detailed images of the inside of your body, without using harmful radiation. In this blog, we will explore the MRI scan machine, the types of MRI scans available, and how MRI scan images are used to diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
An MRI scan is a medical imaging technique that uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed pictures of the organs and tissues inside your body. The primary advantage of MRI over other imaging techniques is that it does not use ionizing radiation like X-rays or CT scans, making it a safer option for imaging soft tissues.
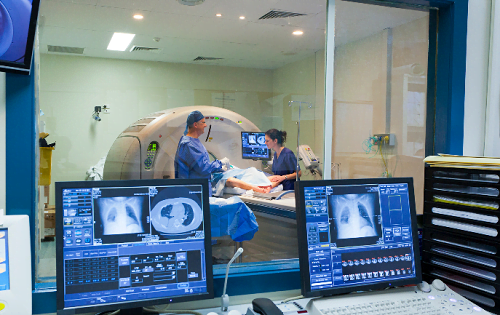
During an MRI scan, the patient is asked to lie down on a table that slides into a large MRI scanner. The scanner generates a strong magnetic field, which aligns the protons in your body. When radio waves are directed at the aligned protons, they emit signals that the MRI machine picks up and converts into MRI scan images. These images provide highly detailed views of the inside of your body, allowing doctors to identify abnormalities like tumors, torn ligaments, or diseases in the brain.
There are several types of MRI scans that doctors use, depending on the area of the body being examined. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Brain MRI
A brain MRI is used to detect issues like brain tumors, strokes, infections, and conditions like multiple sclerosis. It can also help doctors evaluate neurological symptoms such as persistent headaches or memory problems.
2. Spinal MRI
This type of MRI scan focuses on the spine and is often used to diagnose conditions like herniated discs, spinal cord injuries, or infections of the spine. It provides clear images of the spinal cord and surrounding tissues.
3. Joint MRI
A joint MRI is commonly used to examine the knee, shoulder, hip, or other joints for problems like ligament tears, arthritis, or cartilage damage. This MRI scan gives detailed images of soft tissues that X-rays cannot capture.
4. Cardiac MRI
A cardiac MRI evaluates the heart’s function, structure, and blood vessels. It can help detect heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, or congenital heart defects.
5. Abdominal MRI
This scan provides detailed images of the abdomen, helping doctors assess organs like the liver, pancreas, kidneys, and intestines for conditions like cancer, inflammation, or infections.
6. MRI Ankle
Provides detailed images of the ankle joint, tendons, ligaments, and surrounding soft tissues, helping diagnose injuries, arthritis, or infections.
7. MRI Elbow
Focuses on the elbow's complex structure, including bones, tendons, and ligaments, aiding in the detection of tears, fractures, or joint abnormalities.
8. MRI Wrist Joint:
Offers high-resolution images of the wrist, helping identify carpal tunnel syndrome, ligament injuries, or joint degeneration.
9. MRI Neck
Examines the cervical spine and surrounding tissues, essential for diagnosing nerve compression, disc issues, or neck pain.
10. MRI Shoulder
Captures images of the shoulder's muscles, tendons, and joints to identify rotator cuff tears, joint instability, or other injuries.
11. MRI Foot
Provides insights into foot bones, tendons, and soft tissues, useful for diagnosing plantar fasciitis, fractures, or ligament damage.
MRI scans offer many advantages, particularly when compared to other diagnostic tools. Here’s why they’re crucial for modern medicine:
1. Non-invasive and Safe
Since MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves instead of radiation, it is considered a non-invasive and safer method of medical imaging. This makes it an ideal option for patients who need frequent scans or those at risk from radiation exposure.
2. High-Resolution Images
MRI provides very detailed images of the body’s soft tissues, which can be crucial for detecting conditions that might not be visible with other imaging techniques, such as X-rays.
3. Versatility
MRI scans can be used to examine almost any part of the body, from the brain and spine to joints, muscles, and organs like the liver and heart. This versatility makes it a go-to tool for doctors when diagnosing a variety of conditions.
Preparing for an MRI scan is relatively simple, but there are a few things you should keep in mind:
Wear comfortable clothing: You may be asked to change into a hospital gown, especially if you are undergoing an MRI of the chest or abdomen.
Remove metal objects: The MRI machine uses a strong magnetic field, so all metal items (such as jewelry, glasses, and hearing aids) must be removed before the procedure.
Inform the technician: Let the MRI technician know if you have any metal implants, pacemakers, or other devices in your body, as these can interfere with the scan.
In an MRI scan, medical background images are used to provide context to the primary images of your organs or tissues. These background images allow radiologists to distinguish between normal and abnormal structures in the body. They serve as a baseline, which helps doctors better understand the condition being evaluated.
For example, when a brain MRI is performed, the background images may show the brain’s natural anatomy, which helps the radiologist identify abnormal areas, such as tumors or lesions, against the normal tissue.
MRI scans are a critical tool in modern healthcare, providing doctors with detailed images that help diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions. Whether it’s for detecting brain tumors, examining the spine, or assessing joint injuries, MRI scans provide clear, non-invasive views of the body’s internal structures. Understanding the different types of MRI scans, how they work, and what the MRI scan images reveal is essential in making informed decisions about your health.
Regular MRI scans can be crucial in identifying issues early and preventing more severe health complications down the road. If you’re due for an MRI, speak with your healthcare provider to understand the best type of scan for your needs.