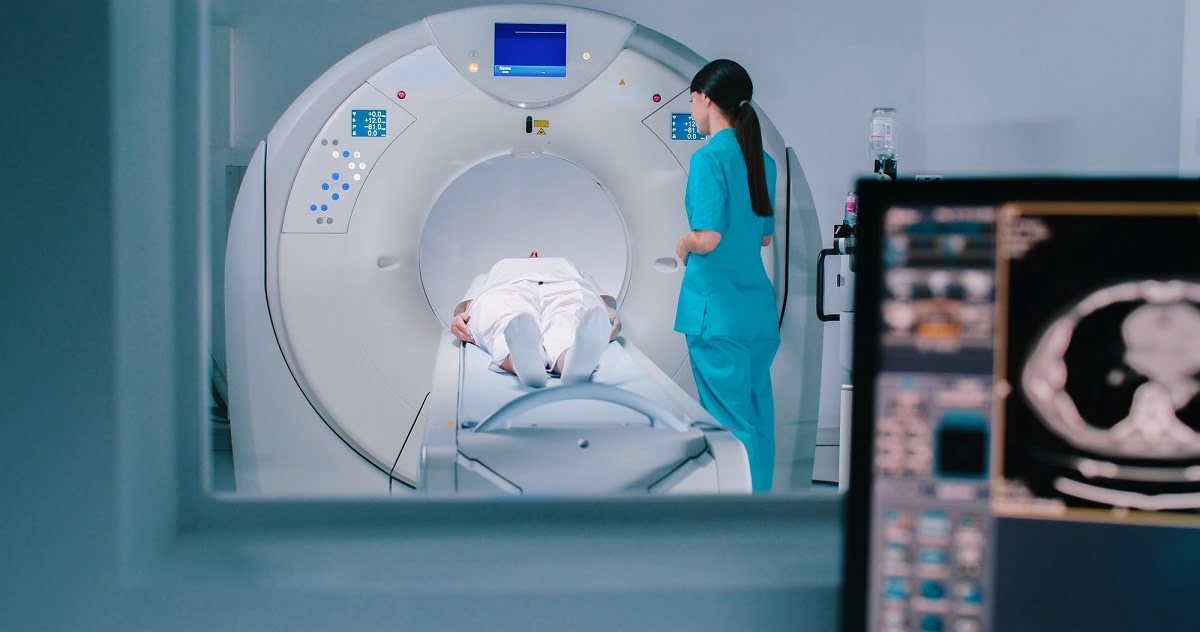
What is a Contrast CT Scan?
A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to create detailed images of the inside of your body.
A contrast dye is injected to highlight organs, blood vessels, and tissues.
This helps doctors detect problems more accurately than a regular scan.
Why is a CT Lower Abdomen Scan Done?
Doctors may recommend this scan if you have:
-
Persistent abdominal pain
-
Suspected kidney stones
-
Infection or inflammation
-
Unexplained swelling
-
Injury to the abdomen
-
Suspected tumors or growths
It helps evaluate organs like:
-
Kidneys
-
Urinary bladder
-
Intestines
-
Blood vessels
-
Reproductive organs
Preparation Before the Scan
Follow these simple steps for accurate results:
Visit Now: https://www.diagnopein.com
-
Do not eat for 4–6 hours before the scan
-
Inform your doctor about allergies
-
Tell the radiologist if you are pregnant
-
Share details of current medicines
-
Drink water unless advised otherwise
You may be asked to remove metal objects like jewelry or belts.
How the Procedure Works
The scan is quick and painless.
-
You lie on a movable scanning table
-
Contrast dye is injected through a vein
-
The table moves through the CT scanner
-
You may be asked to hold your breath briefly
The entire process usually takes 10–20 minutes.
Are There Any Side Effects?
Most people tolerate contrast dye well.
Some may experience:
-
Mild warmth sensation
-
Metallic taste in mouth
-
Temporary nausea
Serious reactions are rare but possible. Always inform staff about allergies.
Cost of CT Scan Lower Abdomen in Pune
The price varies based on diagnostic center, technology, and reporting time.
Typically, the cost ranges from:
?? ?4,000 to ?9,000
Packages may include radiologist reporting and digital images.
After the Scan
You can return to normal activities immediately.
Drink plenty of water to flush out the contrast dye.
Your doctor will review the report and explain the results.
When Should You Book This Scan?
Consider scheduling the scan if you have:
-
Ongoing abdominal discomfort
-
Unclear ultrasound results
-
Doctor’s referral for detailed imaging
Early diagnosis helps in faster treatment and better outcomes.