Why USG Early Anomaly Scan (11–14 Weeks) is Important
The USG Early Anomaly Scan (11–14 Weeks) plays a crucial role in early pregnancy care. It helps in:
-
Identifying early developmental issues in the fetus.
-
Detecting the risk of chromosomal conditions like Down syndrome (commonly using NT measurement).
-
Determining gestational age and confirming the expected date of delivery.
-
Assessing multiple pregnancies (twins or triplets).
-
Evaluating the baby’s heartbeat, placental position, and amniotic fluid levels.
Timely detection of potential abnormalities can lead to early management and better pregnancy outcomes. Expectant mothers are strongly advised to get an early pregnancy scan at 12 weeks for reassurance and medical guidance.
Benefits of USG Early Anomaly Scan (11–14 Weeks)
Undergoing the USG Early Anomaly Scan (11–14 Weeks) offers numerous benefits for both mothers and healthcare providers:
-
Provides an early assessment of fetal health and growth.
-
Helps diagnose any congenital or structural issues at an early stage.
-
Enables accurate dating of pregnancy when compared with the last menstrual period (LMP).
-
Offers emotional reassurance for parents regarding the baby’s development.
-
Reduces anxiety through early screening results, guiding further diagnostic tests if required.
For women at higher risk due to age, previous pregnancy complications, or genetic history, the 11–14 week ultrasound is particularly recommended to rule out anomalies early.
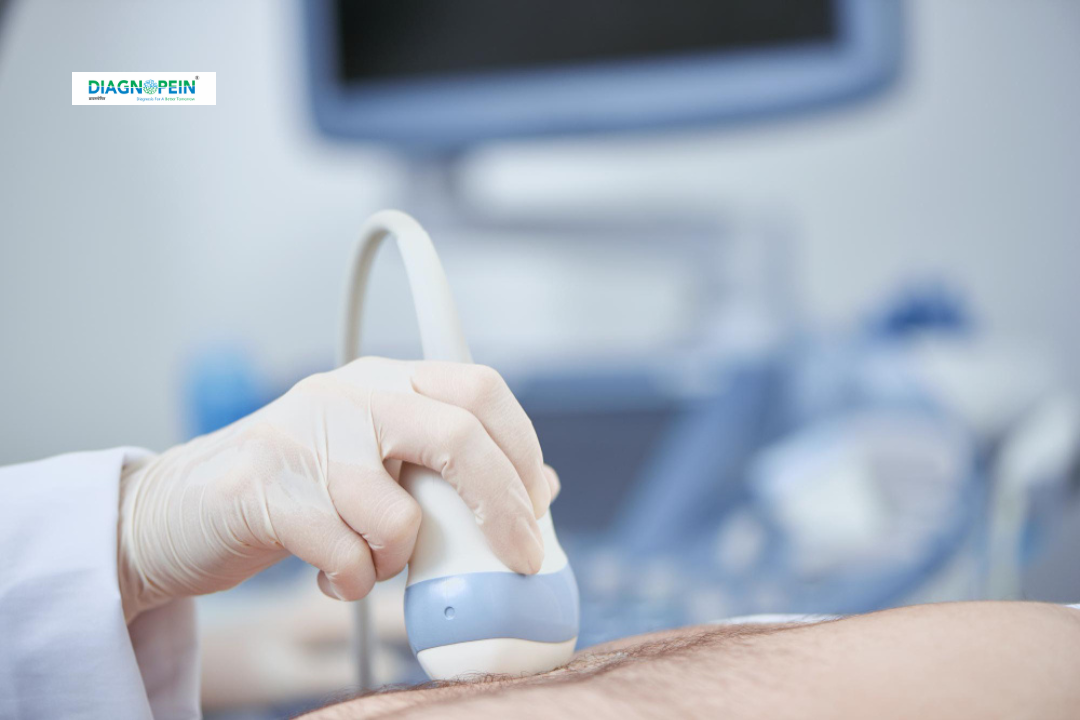
How the USG Early Anomaly Scan (11–14 Weeks) is Done
The USG Early Anomaly Scan (11–14 Weeks) is a simple ultrasound test conducted using a transabdominal approach, though in some cases, a transvaginal scan may be used for clearer imaging.
Procedure:
-
You will be asked to lie comfortably on the examination bed.
-
A small amount of gel is applied to the lower abdominal area.
-
The ultrasound probe moves gently over the abdomen to capture detailed fetal images.
-
The radiologist or sonologist observes fetal structures, heartbeat, neck fold thickness (NT), and nasal bone presence.
-
The results are interpreted to identify any possible anomalies.
This entire process usually takes 20–30 minutes and poses no risk to the mother or baby.
Scan Parameters and Findings
During the 11–14 week scan, the following key parameters are evaluated:
-
Crown-Rump Length (CRL): Assesses fetal growth and gestational age.
-
Nuchal Translucency (NT): Measures fluid at the back of the baby’s neck, a key marker for chromosomal anomalies.
-
Nasal Bone Visualization: Important for screening Down syndrome risk.
-
Foetal Heart Rate (FHR): Determines normal cardiac activity.
-
Placental Position: Early check for proper implantation.
-
Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI): Ensures adequate fluid levels around the baby.
These parameters collectively provide a detailed fetal health overview, helping doctors plan the next stages of pregnancy care.
Keywords and Search Optimization (High-Volume, Low-Difficulty)
Key SEO terms naturally embedded in the text include:
USG Early Anomaly Scan, 11–14 week scan, NT scan, First Trimester Ultrasound, Early Pregnancy Ultrasound, Fetal anomaly scan at 12 weeks, Ultrasound in Karad, Pregnancy scan 11 weeks, Prenatal screening Karad, USG scan for fetal growth.