Why USG Carotid Doppler Study is Important
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are among the leading causes of health complications globally. Performing a USG Carotid Doppler Study helps identify early arterial blockages, allowing preventive action before serious events like stroke occur.
Doctors recommend this test if you experience dizziness, vision problems, numbness, or a transient ischemic attack (mini-stroke). It is also advised for individuals with hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of vascular disease.
This study helps gauge the carotid artery blood flow, detect plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), and assess the risk of future clot formation. In people with previous surgeries or stenting, serial Carotid Doppler Ultrasound Tests help monitor arterial patency and overall vascular health.
Benefits of USG Carotid Doppler Study
The USG Carotid Doppler Study offers numerous diagnostic benefits without involving radiation or contrast media. It is completely safe, non-invasive, and painless, making it suitable for all age groups.
Key advantages include early detection of carotid artery blockages, evaluation of stroke risk, guidance before cardiac or vascular surgery, and assessment of stent or graft conditions.
Since this procedure uses real-time imaging, doctors can quickly identify abnormal flow patterns and decide on appropriate medical or surgical interventions. The Carotid Artery Doppler Ultrasound is also useful for ongoing monitoring of chronic vascular disease, improving preventive care outcomes.
Procedure and Parameters of Testing
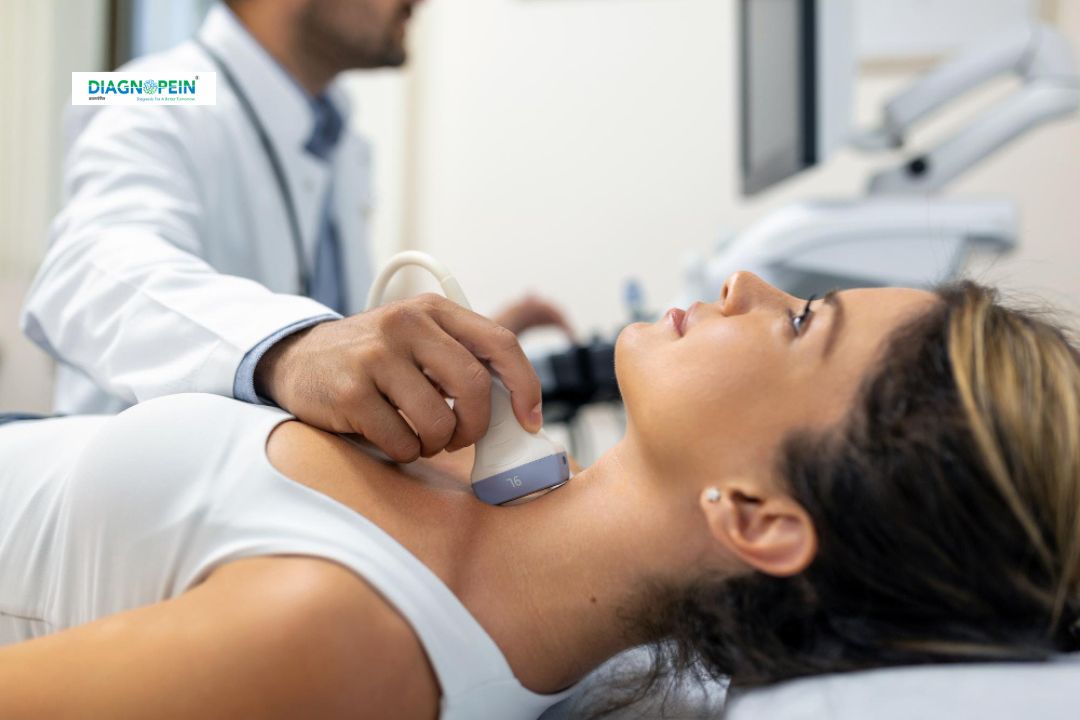
During the USG Carotid Doppler Study, you will lie comfortably on a couch while a radiologist applies a small amount of gel to your neck. A handheld probe called a transducer is moved along both sides of your neck to capture images and measure blood flow.
The total scan time is about 20–30 minutes. Normal blood flow velocities are compared against standard reference values to identify potential narrowing or blockage.
Important parameters assessed include Peak Systolic Velocity (PSV), End-Diastolic Velocity (EDV), Intima-Media Thickness (IMT), and Plaque Morphology. The test also evaluates the vertebral arteries, which contribute to brain blood supply.