Diagnopein X-RAY CHEST +OBLIQUE VIEW (Walkin DHPL) - CIMS Bhopal Centre in Bhopal
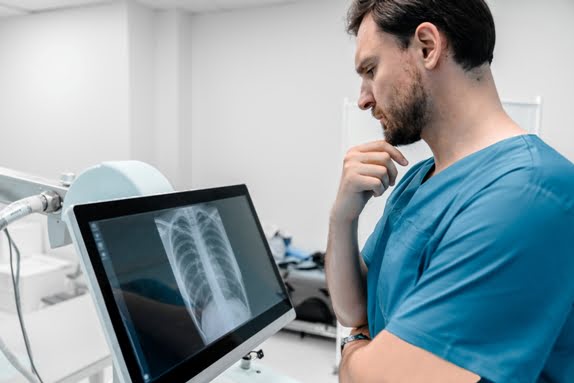
An X-ray Chest + Oblique View is an imaging procedure that combines a standard chest X-ray with additional oblique views to provide a more comprehensive examination of the chest area, including the lungs, heart, ribs, and surrounding structures. This combination of views allows healthcare providers to gain a clearer understanding of the patient’s condition, especially when the standard chest X-ray doesn’t provide enough detailed information. This procedure is particularly useful in diagnosing various chest-related conditions, including lung infections, tumors, fractures, and cardiac abnormalities.








