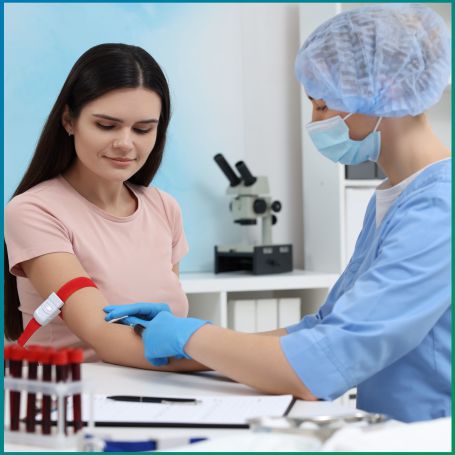
One of the most accurate ways to detect such infections is through a fungal culture test of the vitreous fluid, known as a vitreous tap.

A fungal culture test is a laboratory procedure that helps detect fungal infections. When dealing with suspected fungal infections in the eye, especially within the vitreous humor (the clear gel-like substance inside the eye), a vitreous tap is performed to obtain a sample. The collected sample is then cultured in a lab to identify the specific fungus causing the infection. A fungal culture and sensitivity test can be performed on the sample, which not only confirms the fungal presence but also helps doctors determine which antifungal medication will be most effective in treating the infection.
The fungal culture test via a vitreous tap is conducted when there is a suspicion of a fungal eye infection, particularly when the patient has persistent eye inflammation, redness, or pain, Vision is deteriorating without a clear cause. There is a history of eye surgery, trauma, or an immunocompromised condition that increases the risk of infection. Standard treatments for bacterial infections have failed, indicating the possibility of fungal involvement. This test is essential because fungal infections in the eye can be elusive and often mimic other conditions. If not accurately diagnosed, these infections can lead to permanent vision impairment or even blindness.
The following individuals should consider undergoing a fungal culture and sensitivity test via vitreous tap Patients with symptoms of fungal eye infections, such as blurred vision, pain, redness, or persistent inflammation.Individuals who have undergone recent eye surgery, particularly those who experience post-operative complications. Patients with underlying conditions that compromise their immune system, such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer, as these conditions increase susceptibility to fungal infections. People who have suffered trauma to the eye or have been exposed to environments prone to fungal growth. Early detection and treatment are critical to preserving vision in these cases.
At Diagnopein, we prioritize accurate and timely diagnosis to ensure you receive the best care possible. Here are some reasons why Diagnopein is the best choice for fungal culture tests in Pune:
Expertise in Ophthalmic Fungal Infections: Our team includes specialists in diagnosing and managing fungal infections, ensuring your test results are handled by experienced professionals.
Advanced Laboratory Facilities: We utilize cutting-edge technology for the fungal culture and sensitivity test, ensuring precise and reliable results.
Fast Results: Timely results are critical for preventing the progression of fungal infections in the eye. Diagnopein ensures a quick turnaround for your fungal culture test results.
Affordable Testing: We offer competitive pricing, and the fungal culture test price in India at Diagnopein is transparent and budget-friendly.
1. Culture Method
2. Sample
3. Colony Count
4. Organism(s) Isolated
5. Culture Report: Culture yields growth of
6. Culture isolated after 7 days :
7. Culture isolated after 14 days:
8. Culture isolated after 21 days:
9. Ampicillin
10. Amikacin
11. Amoxicillin clavulanate
12. cefoperazon+sulbactam
13. Cefuroxime
14. Cefepime
15. Cefotaxime
16. Ciprofloxacin
17. Ertapenem
18. Gentamicin
19. Imipenem
20. Meropenem
21. Norfloxacin
22. Nitrofurantoin
23. Piperacillin-tazobactam
24. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (Cotrimoxazole)
The results of a fungal culture and sensitivity test can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on how quickly the fungus grows in the lab.
A small needle is used to collect a sample of vitreous fluid from the eye. The sample is then sent to a lab for culturing and analysis to identify any fungal organisms present.
The vitreous tap is a minor procedure performed under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. Patients may experience slight pressure, but significant pain is uncommon.
A fungal culture test via vitreous tap involves collecting a small sample of vitreous fluid from the eye to detect the presence of fungal infections.